Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) can cause side effects. In this section, you can read about the most common ones. The side effects you may experience vary from person to person. For example, what about headaches? Or memory problems? And what can be done about them?
What are the most common side effects of ECT?
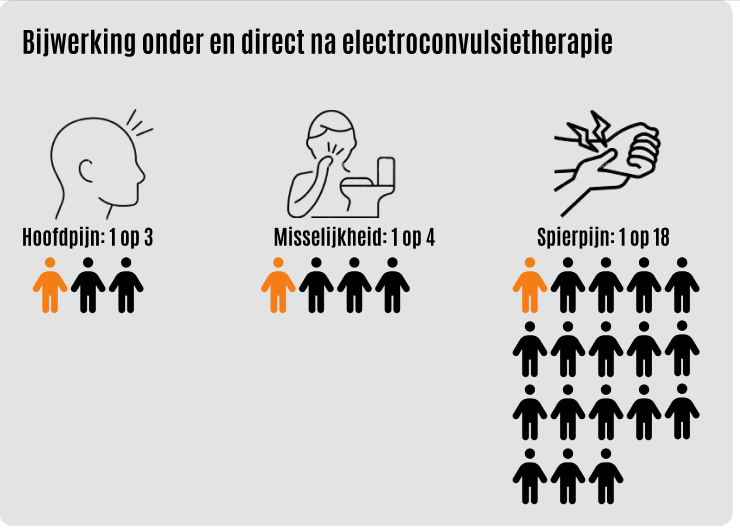
Some people experience temporary side effects during or shortly after treatment. These may include Headache, nausea, fatigue, muscle aches, dizziness and trouble remembering events around the time of treatment.For instance, someone might not recall what they ate the night before or that a family member came to visit. Others may feel a little confused or have trouble concentrating for a short period. On the other hand, some notice they function better as their depression improves. Everyone’s experience is different.
What are the memory-related side effects of ECT?
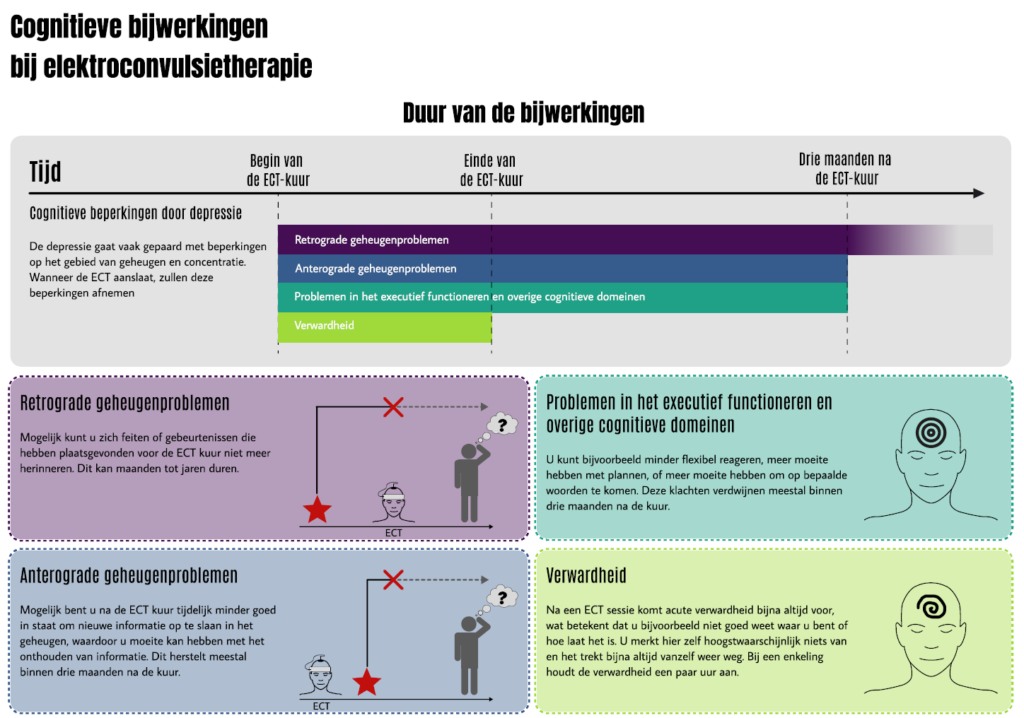
Memory problems—also called cognitive side effects —are another possibility. It is important to know that ECT does not cause brain damage. For most people who experience memory or concentration problems, these issues improve within about three to four weeks after treatment ends.
Only a small number of people have long-lasting side effects. The most common are memory problems and reduced concentration. Some people lose specific memories from the past. In rare cases, concentration problems may persist for longer.
The images below explain the different types of memory and concentration problems and show that most of these issues are resolved three months after ECT.
The impact of memory problems varies for each individual and depends on their situation. For example, a small memory lapse while cooking at home might have little consequence, while a similar mistake at work could be more serious —especially depending on the type of job. It’s important to discuss these problems with your support network and your healthcare providers.
How do side effects influence the choice for ECT?
When choosing a treatment, it’s important to weigh how severely depression affects a person’s life against the potential side effects. People who receive ECT often have severe depression and may experience a significant improvement in quality of life as their symptoms decrease.
However, memory problems—especially when they last for a longer time—can be difficult to cope with. This can make it harder to opt for ECT, even though it often provides rapid relief from symptoms for most people without causing permanent side effects.
What can be done to reduce the side effects of ECT?
The ECT team closely monitors the side effects of each patient. If necessary, they adjust the treatment.
For example: if a patient experiences nausea, they can be given anti-nausea medication before anaesthesia. For headaches, painkillers can be given two hours before the treatment. If memory problems occur, the team can adjust the electrode placement or reduce the number of treatments per week.



